Basic Concepts
This document introduces the core concepts in ETOfflineToolkit that are also applicable to ET.
What is ETOfflineToolkit?
Introduction
ETOfflineToolkit is a toolkit derived from the ET framework focusing on single-player game development. It inherits the excellent design philosophy of the ET Framework and provides developers with a complete set of development tools.
Core Features
- Single-Player Specialized: The single-player portion extracted from the
Unity Dual-End ETframework - Architectural Design: Fully preserves the powerful core architectural design and development philosophy of the
ETframework - Feature-Rich: Retains powerful features from the
ET EUIframework such as EUI system, object pool, and resource management - Developer-Friendly: An ideal choice for developers who want to use
ETto develop single-player games
ECS Architecture Design
What is ECS?
ECS (Entity-Component-System) is a data-driven architectural pattern that breaks down game objects into three core concepts:
- Entity: The basic object in the game, containing only a unique identifier
- Component: Pure data attached to entities, defining entity properties and states
- System: Logical units that process specific component combinations, responsible for game logic execution
ECS Tree Structure Design
ET's design creates a tree-like structure with clear hierarchy, making it very easy to understand the entire game architecture. The top layer Game.Scene, also known as Root, has different module data mounted on it. Root can then mount Scenes, referred to as CurrentScene, and each module itself can mount many data elements. When developing a new feature, you don't need to think too much about how to design classes, where to put data, whether mounting here will cause redundancy, etc.
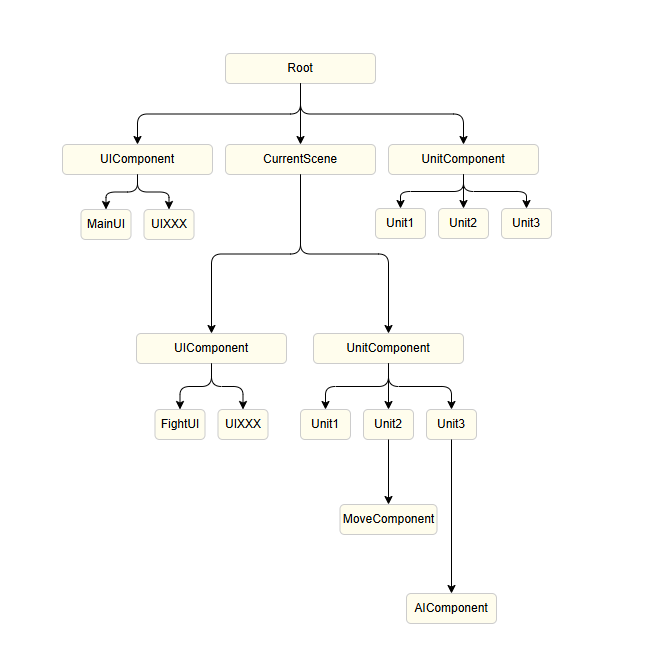
Introduction
The ET framework uses a clear tree structure design, which makes the game architecture hierarchical, easy to manage and extend.
Overall Structure
Root
├── UIComponent
│ ├── MainUI
│ └── UIXXX
├── CurrentScene
│ ├── UIComponent
│ │ ├── FightUI
│ │ └── UIXXX
│ └── UnitComponent
│ ├── Unit1
│ ├── Unit2 (with MoveComponent)
│ └── Unit3 (with AIComponent)
└── UnitComponent
├── Unit1
├── Unit2
└── Unit3Core Node Description
Root (Root Node)
Root Node
- Serves as the root node of the entire scene tree
- Manages global components and systems
- Can mount multiple top-level components
UIComponent (UI Component)
UI Management
- Responsible for managing all UI-related content
- Can exist at both Root and CurrentScene levels
- UIComponent under Root manages global UI
- UIComponent under CurrentScene manages scene-related UI
CurrentScene (Current Scene)
Scene Management
- Represents the currently active game scene
- Contains scene-specific UI and units
- Serves as a container for scene-related components
UnitComponent (Unit Component)
Unit Management
- Manages all game units in the scene
- Can exist at both Root and CurrentScene levels
- Supports mounting specific functional components (such as MoveComponent, AIComponent)
Design Advantages
Architecture Benefits
Clear Hierarchy
- Tree structure is intuitive and easy to understand
- Component relationships are clear at a glance
- Easy to understand and maintain
Strong Extensibility
- Easy to add new components
- Supports dynamic mounting and unmounting
- Flexible component combinations
Convenient Management
- Unified component management method
- Clear lifecycle control
- Convenient component finding and accessing
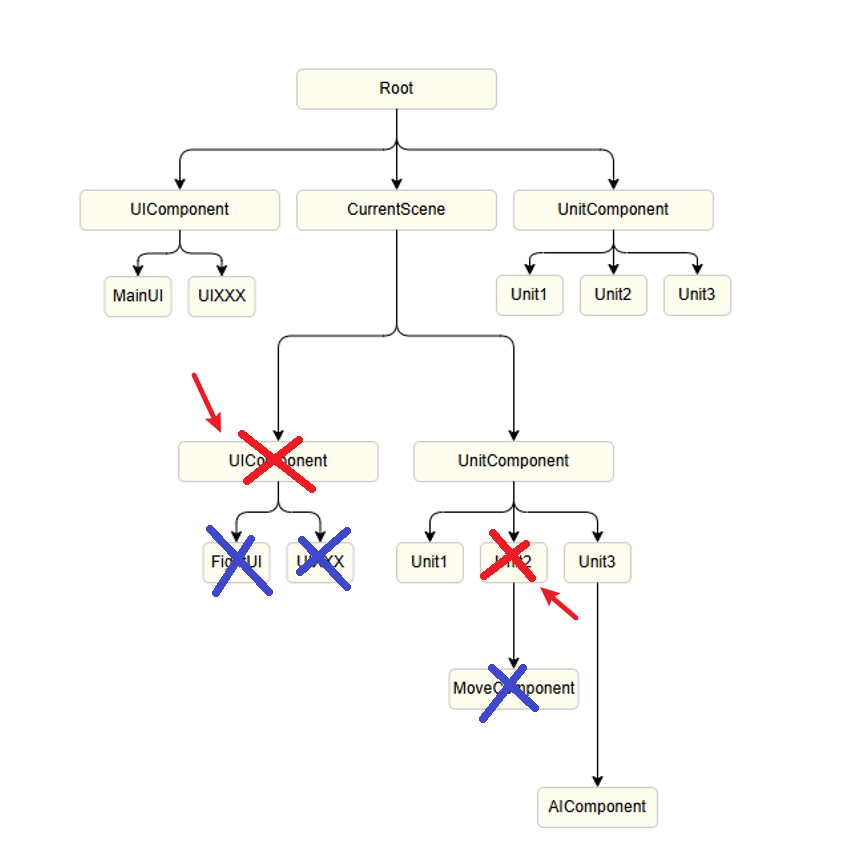
Component Lifecycle
Node Removal
- If an entity or component is removed (Disposed), all components and child entities under it will also be removed (Disposed)
- Removed components will trigger the corresponding Dispose callback
Technical Support
Get Help
- 💬 Join QQ group for discussion
(ET Framework Group): 474643097 - ⭐ Follow the project on GitHub for the latest updates